How to Build an App Like TripPlanner
Travel planning has been transformed in the age of digital ease by smartphone apps that help consumers plan and manage…
Many projects are underway using Blockchain technology to improve supply chain transparency and monitor prove-nance. These initiatives amass data about how goods are made, where they come from, and how they are managed; this information is stored in the blockchain-based system. This means that the data becomes permanent and easily shared, giving supply chain players more comprehensive track-and-trace capabilities than ever before. Companies can use this information to provide proof of legitimacy for products in pharmaceutical shipments, for example, and proof of authenticity for luxury goods. These initiatives also deliver consumer benefits – people can find out more about the products they are buying, for example, whether a product has been ethically sourced, is an original item, and has been preserved in the correct conditions.
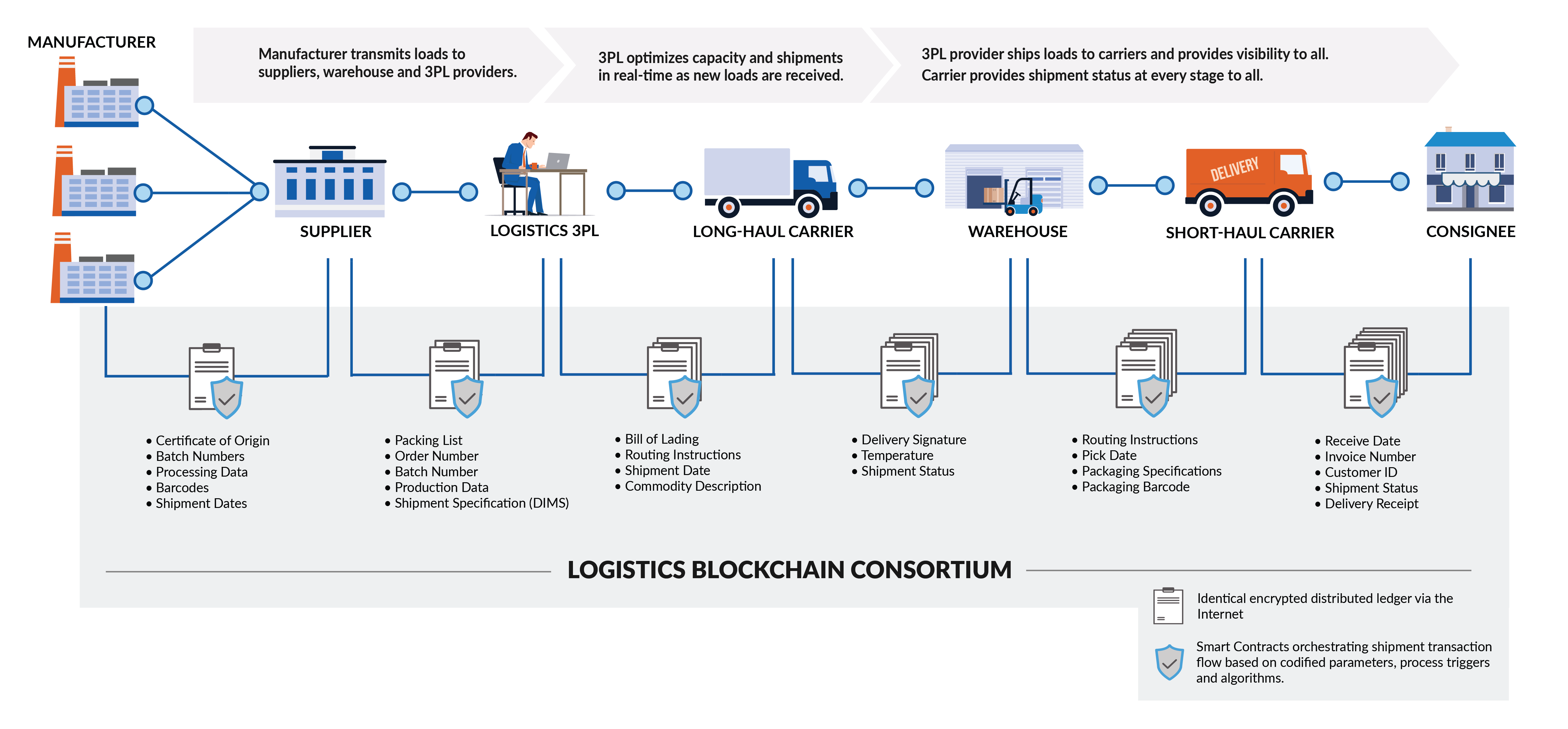
Achieving excellence in logistics involves working collabo-ratively with others to optimize the flow of physical goods as well as the complex flow of information and financial transactions.
But today there is a significant amount of trapped value in logistics, largely stemming from the fragmented and competitive nature of the logistics industry. For example, in the US alone, it is estimated that there are over 500,000 individual trucking companies.8 With such a huge number of stakeholders involved in the supply chain, this often creates low transparency, unstandardized processes, data silos and diverse levels of technology adoption.
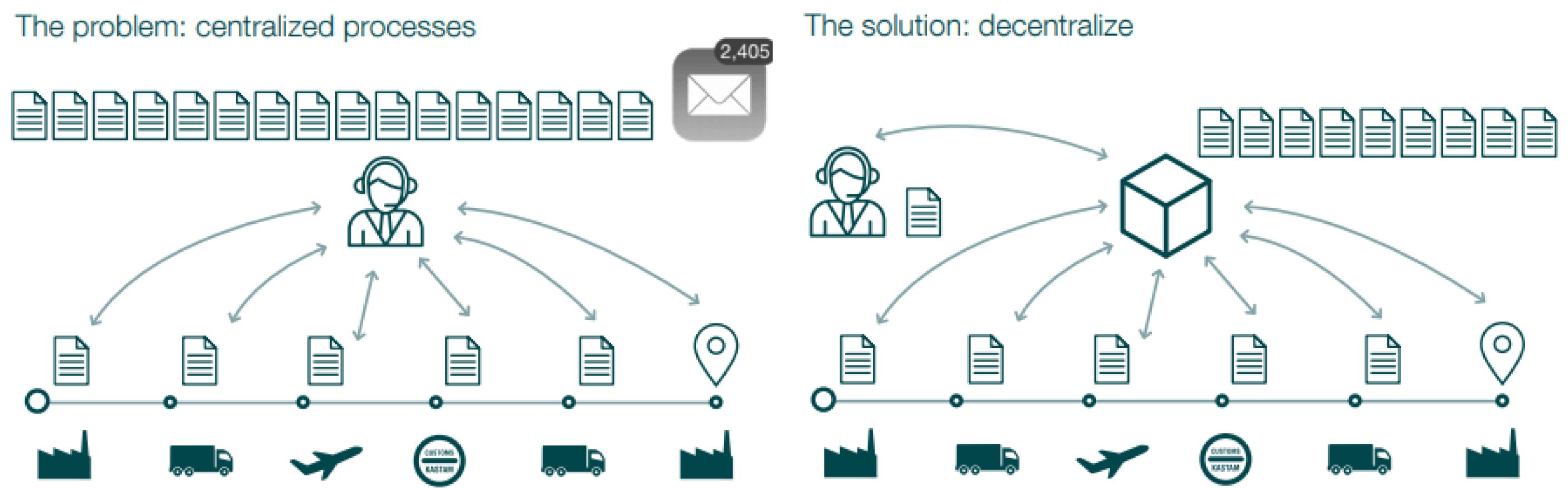
Many parts of the logistics value chain are also bound to manual processes mandated by regulatory authorities. For example, companies must oftentimes rely on manual data entry and paper-based documentation to adhere to customs processes. All this makes it difficult to track the provenance of goods and the status of shipments as they move along the supply chain, causing friction in global trade. Blockchain can potentially help to overcome these frictions in logistics and realize substantial gains in logistics process efficiency. This technology can also enable data transparency and access among relevant supply chain stakeholders, creating a single source of truth. In addition, the trust that is required between stakeholders to share information is enhanced by the intrinsic security mecha-nisms of blockchain technology.
Furthermore, blockchain can achieve cost savings by pow-ering leaner, more automated, and error-free processes. As well as adding visibility and predictability to logistics operations, it can accelerate the physical flow of goods. Provenance tracking of goods can enable responsible and sustainable supply chains at scale and help to tackle prod-uct counterfeiting. Additionally, blockchain-based solu-tions offer potential for new logistics services and more innovative business models. Some of the most prominent use cases for blockchain in the areas of global trade logistics, supply chain transparency and traceability, and commercial processes in logistics (see figure 15 on next page). The final part of this chapter outlines the key success factors for industry adoption of the technology.

Travel planning has been transformed in the age of digital ease by smartphone apps that help consumers plan and manage…

Introduction Mobile apps are now essential tools for tourists looking for speed, efficiency, and customised experiences in the fast-paced world…

Introduction Mobile applications, which meet a variety of requirements and interests, have become an essential part of our lives in…